Manufacturing is a key pillar and a major force behind Indonesia’s economic growth. This is clearly illustrated by its significant contribution to the country’s GDP, which reached 16.30% in the second quarter of 2023. This figure is the highest among all sectors, surpassing those of agriculture, construction, and mining.
Furthermore, the value of manufactured exports has shown remarkable growth, maintaining a streak of positive performance for 43 consecutive months. Consequently, the trade surplus grew to USD 2.41 billion, equivalent to approximately IDR 37.9 trillion, as of November 2023.
Given these encouraging developments, the question remains: How does the Manufacturing Sector drive Indonesia’s Economic Growth?
In this article, the Bawalaksana Central Industrial team will examine the impact of the manufacturing sector on driving domestic economic growth and explore strategies for ensuring that this upward trend continues.
Why is the manufacturing industry so vital to Indonesia’s economy?
The manufacturing industry is crucial to Indonesia’s economy, as it boosts productivity and enhances job quality. To fully realize the potential of this sector, it is essential to have supportive regulations, diverse business opportunities, access to resources, a favorable investment climate, and a skilled workforce. These elements are crucial for fostering growth and sustainability within the industry.
What factors are driving industrial growth in Indonesia?
The expansion of industrialization in Indonesia is fueled by several crucial factors, including the availability of land, a skilled labor force, access to capital, technological advancements, and reliable connectivity.
What is the Manufacturing Industry?
Manufacturing broadly refers to the processes by which businesses convert raw materials into finished or semi-finished products, relying on machinery and human labor.
According to Britannica, a manufacturing company systematically produces goods from raw materials, utilizing either manual labor or automated systems, often with a division of labor.
This sector stands out from other types of businesses, such as trading or service industries, due to its complex production processes, advanced technologies, and machinery.
Manufacturing is vital to economic growth and a key driver of job creation. It spurs innovation, drives technological advancements, and, most importantly, creates job opportunities for a diverse workforce.
Transforming raw materials into finished goods raises the economic value of products. Furthermore, manufacturers engaging in industrial downstream processes significantly enhance their profit potential. This approach brings products closer to end consumers and opens up a wider range of export opportunities at competitive prices.
Notably, Indonesia is a treasure trove of raw materials sought after by leading global manufacturers, particularly for items such as electric vehicle batteries, stainless steel, and computer chips.
The demand for these materials continues to rise with technological advancements and the growth of Artificial Intelligence (AI). This trend is promising for the manufacturing sector and is expected to drive significant domestic economic development, as well as enhance the international market value of Indonesian products.

The Manufacturing Sector’s Role in GDP
As the crucial driving force behind Indonesia’s national economy, the manufacturing sector is essential to its economic framework. Here are some key insights into how this sector contributes to the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
Key Driver of the Economy
In the second quarter of 2023, the manufacturing sector emerged as the most significant contributor to Indonesia’s GDP, accounting for 16.30%. This performance outstripped other sectors, including agriculture, trade, mining, and construction, underscoring the sector’s crucial role in the national economy.
Minister of Industry Agus Gumiwang Kartasasmita stated, “The manufacturing sector continues to lead in contributions compared to other industries, demonstrating that our manufacturing landscape is strong despite a global economic slowdown. This encouraging trend aligns well with Indonesia’s Manufacturing PMI and the Industrial Confidence Index, which remain in the expansion zone,” as the Ministry of Industry reported on August 8, 2023.
Efforts to Boost Contributions
Agus Gumiwang Kartasasmita, Indonesia’s Minister of Industry, has set an ambitious goal to elevate the manufacturing sector’s contribution to 20% by 2024, following a decline in the previous year. Achieving this target is feasible through well-planned initiatives, such as government stimulus packages and pro-business policies.
One key positive outcome anticipated from these efforts is a resurgence of industrial enthusiasm, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic’s effects.
A report by S&P Global reveals that Indonesia’s Manufacturing PMI has remained above the 50-point threshold for seven consecutive months as of April 2023, signaling ongoing expansion.
For context, the PMI (Purchasing Managers’ Index) serves as a key economic indicator that tracks business trends in both the manufacturing and service sectors. This index comprises several crucial components, including:
- New orders
- Inventory levels
- Production output
- Supplier deliveries
- Employment

The Impact of Manufacturing on Exports and the Trade Balance
As highlighted earlier, industrial downstreaming significantly contributes to product value, establishing the manufacturing sector as the leading driver of economic growth compared to other industries.
The benefits of these downstream efforts are evident in Indonesia’s trade balance, reflected in the ongoing prominence of manufactured goods in the country’s export achievements.
This upward trend has been consistent for 43 months, with the trade surplus reaching USD 2.41 billion, equivalent to approximately IDR 37.9 trillion, in November 2023, as reported by Data Indonesia.
It’s essential to recognize that the improvement in the trade balance stems from a structural shift in Indonesia’s exports—from a heavy reliance on commodity exports to a greater focus on manufactured products. Alongside downstreaming, the P3DN program (Program to Increase the Use of Domestic Products) has also played a crucial role in enhancing the domestic trade balance.
“Indonesia’s export landscape has transformed since the onset of downstreaming, leading to an increase in processed nickel exports and a diversification in base metal exports,” remarked Mohammad Faisal, Executive Director of the Center of Reform on Economics (CORE), as quoted by Bisnis.com.
He further emphasized, “We’re starting to see the fruits of downstreaming. Although our current processing level is still in its early stages and has ample room for growth, it positions us better than simply exporting raw materials. However, we must remain vigilant; if we get complacent now, other countries may capture the greater added value. It underscores the necessity for ongoing evolution in downstreaming.”
It’s also crucial to understand that the trade balance is influenced by the volume of raw materials imported as primary inputs for domestic manufacturing processes.
Nevertheless, technological advancements in automation within the manufacturing sector can greatly enhance cost efficiency and productivity, making these manufactured goods more competitive in international markets.
The Ministry of Industry’s commitment to enhancing the value and diversity of manufactured exports demonstrates a dedicated effort to stimulate economic growth through the pivotal role of the manufacturing sector.
Investment in the Manufacturing Sector
Investment in the manufacturing sector has been increasing year after year. According to Indonesia.go.id, total assets in 2023 reached IDR 571.47 trillion, and are expected to rise to IDR 630.57 trillion by 2024.
Here are a few key points regarding investments in manufacturing:
- Growing Investment: There has been a notable surge in investments within the manufacturing sector, showcasing investor confidence in the industry’s long-term potential.
- Economic Impact: The influx of capital in this sector directly contributes to increased production, enhanced exports, and the creation of job opportunities, ultimately driving national economic growth.
- Encouraging Innovation: Through ongoing investments, the manufacturing industry is encouraged to innovate, boost efficiency, and adopt technological advancements to maintain its competitive edge in the global marketplace.
Government Support for the Manufacturing Sector
To strengthen the manufacturing sector as a cornerstone of the economy, the Indonesian government has taken significant steps to rejuvenate this vital industry. Here are some of the key initiatives that have been put into action:
Revitalization of the Manufacturing Sector
The Indonesian government has implemented strategic measures to revitalize the manufacturing sector, notably through the Making Indonesia 4.0 roadmap. This initiative is designed to prepare the industry for the challenges of the Industry 4.0 revolution, ensuring it continues to drive the country’s economic growth, attract investment, and boost exports.
“Presently, the industrial sector makes up 20% of our GDP, contributes around 30% to government tax revenues, and accounts for 74% of exports. The biggest contributions come from the five manufacturing sectors outlined in Making Indonesia 4.0,” stated Minister of Industry Airlangga Hartarto during the 2019 Indonesia Economic Outlook discussion in Jakarta.
Clean Energy Transition (Decarbonization)
The Indonesian government is actively supporting the decarbonization of the manufacturing sector to foster a cleaner energy transition. Rapid industrial growth often coincides with an increased reliance on fossil fuels, such as coal, petroleum, and their derivatives, including natural gas and methane.
In light of this, the Indonesian government is dedicated to implementing measures to reduce Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, to cut emissions by 29% by 2030.
The Indonesian government can reach this ambitious target with several key actions that have been put into motion, including:
- Promoting energy efficiency
- Strengthening renewable energy infrastructure
- Diminishing the reliance on fossil fuels
Enhancing Workforce Skills Development
Programs to boost workforce skills are being implemented to address the industry’s changing demands. With a skilled and capable workforce, the national industry can thrive and become more competitive.
Workforce skills development is implemented through various strategies, including competency-based education and partnerships with organizations like the Indonesian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (Kadin), industrial associations, the Ministry of Manpower, and the Ministry of Education and Culture.

Harnessing Industry 4.0 for Enhanced Efficiency
The swift advancement of technology and industrial innovation in today’s world should be a significant driver for adopting Industry 4.0 infrastructure. As a result, the positive impact of manufacturing on Indonesia’s GDP is becoming increasingly apparent and continues to grow.
Embracing Industry 4.0 in the manufacturing sector is poised to significantly boost efficiency and productivity. This will lead to faster production processes and ensure competitive pricing in the global market.
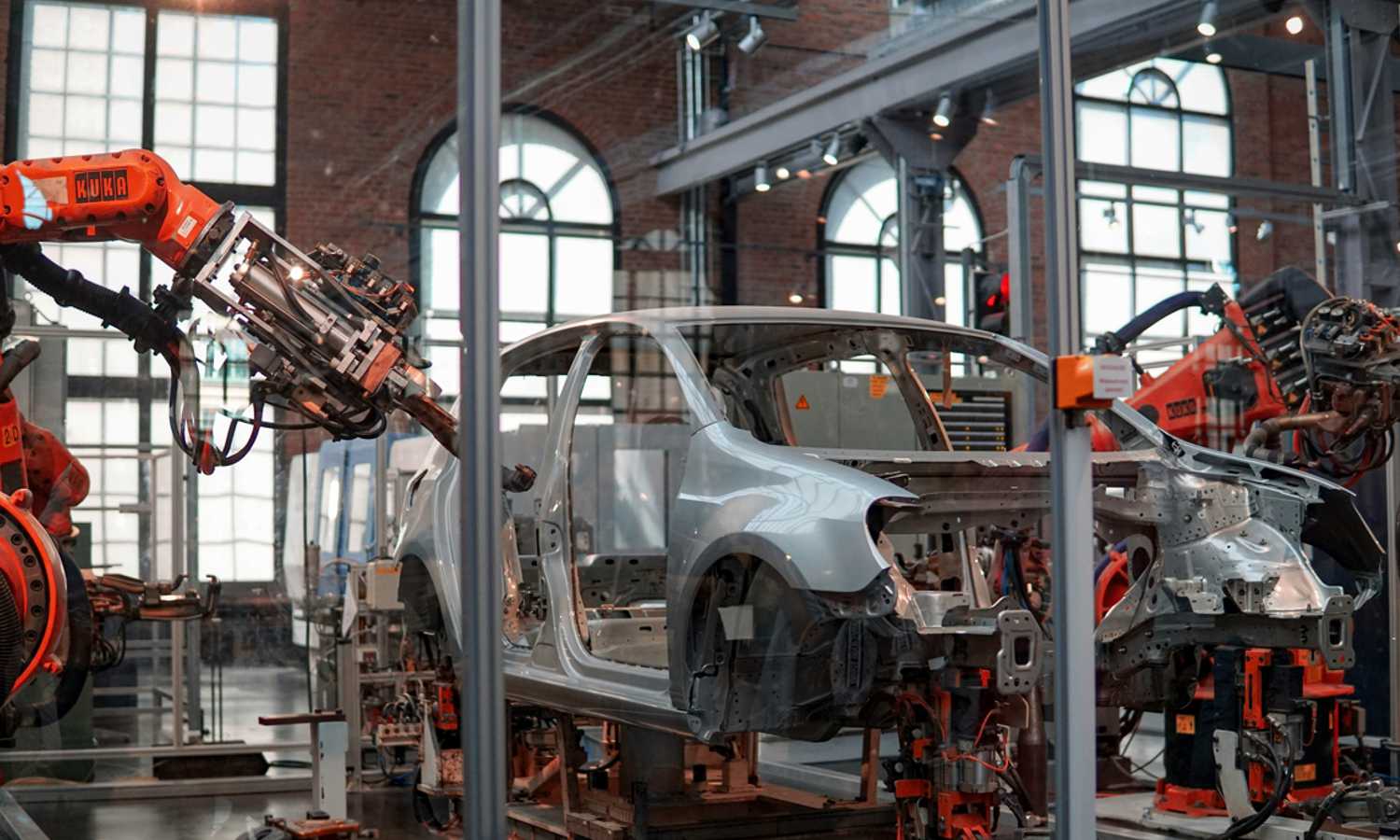
Integrating advanced technology and automation systems allows production to occur automatically and seamlessly.
Key technologies that play a role in the implementation of Industry 4.0 include:
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Big Data
- Cybersecurity
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Additive Manufacturing
- System Integration
- Cloud Computing
- And more
In practice, Pneumatic Systems are extensively utilized in the manufacturing sector for automation. This technology has already found applications across various domestic industries, including food and beverage (F&B), automotive, pharmaceuticals, plastics and packaging, chemicals, and original equipment manufacturing (OEM).
In this digital age, pneumatic systems increasingly integrate intelligent technology and advanced sensors, enabling comprehensive control and synergy with other systems throughout manufacturing.
Although pneumatic systems were first introduced as early as 10 AD and saw significant development in the 19th century, they continue to evolve and innovate today. Ultimately, these rapid advancements in pneumatics will propel industries toward remarkable transformations.

As millennial generation members, we share a natural concern for pressing issues that affect our world. We need to stay informed about every change and development happening around us.
We wholeheartedly support progress in industrial and manufacturing and look forward to tangible growth in our domestic economy.
PT. Bawalaksana Central Industrial, a company that supplies industrial automation parts, is encouraged by the positive trends within the manufacturing sector. This progress enables us to actively contribute to the industry and help boost Indonesia’s GDP.
After reading this article, we encourage you to read our article “Pneumatic System Applications in Electronics Manufacturing and Their Functions” for an enlightening discussion about the crucial role of pneumatic systems in the electronics manufacturing sector.
In conclusion, we’ve examined the importance of manufacturing in Indonesia’s economy. We hope to see more domestic manufacturers embrace Industry 4.0, which will significantly elevate productivity to new heights.
The more manufacturers that adopt Industry 4.0, the greater their contribution to Indonesia’s GDP, especially in non-oil and gas sectors, and the national trade balance.
If your company wants to elevate manufacturing productivity through modern automation technologies, don’t hesitate to consult our engineering team. Click the consultation button below to receive top-notch recommendations from our experts.






![10+ Examples of Pneumatic Tools in Daily Life and Industry [2025]](https://bawalaksana.co/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Sandblasting-large-diameter-pipes-to-remove-surface-contaminants-1080x675.jpg)