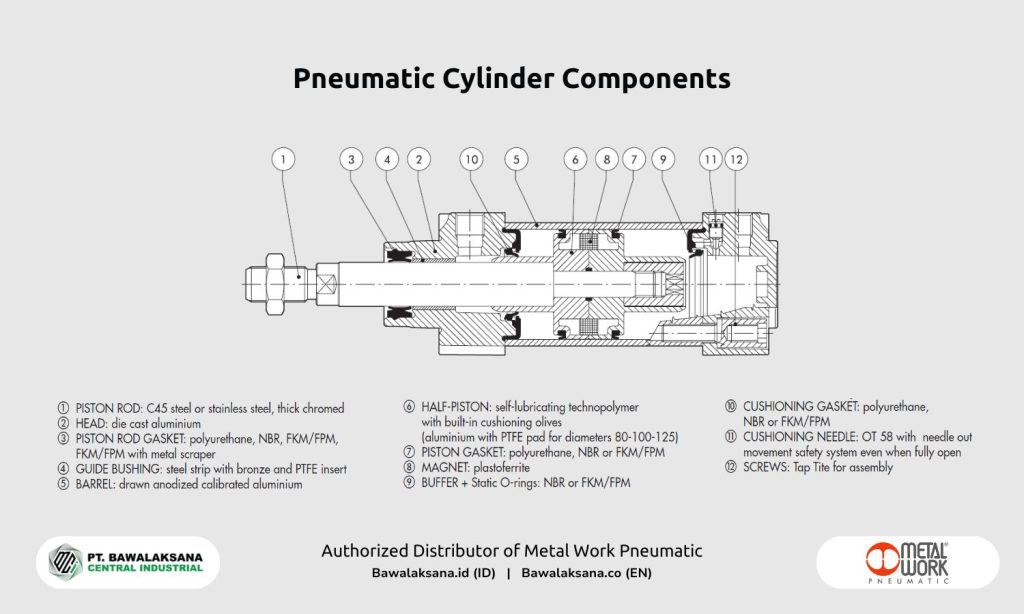
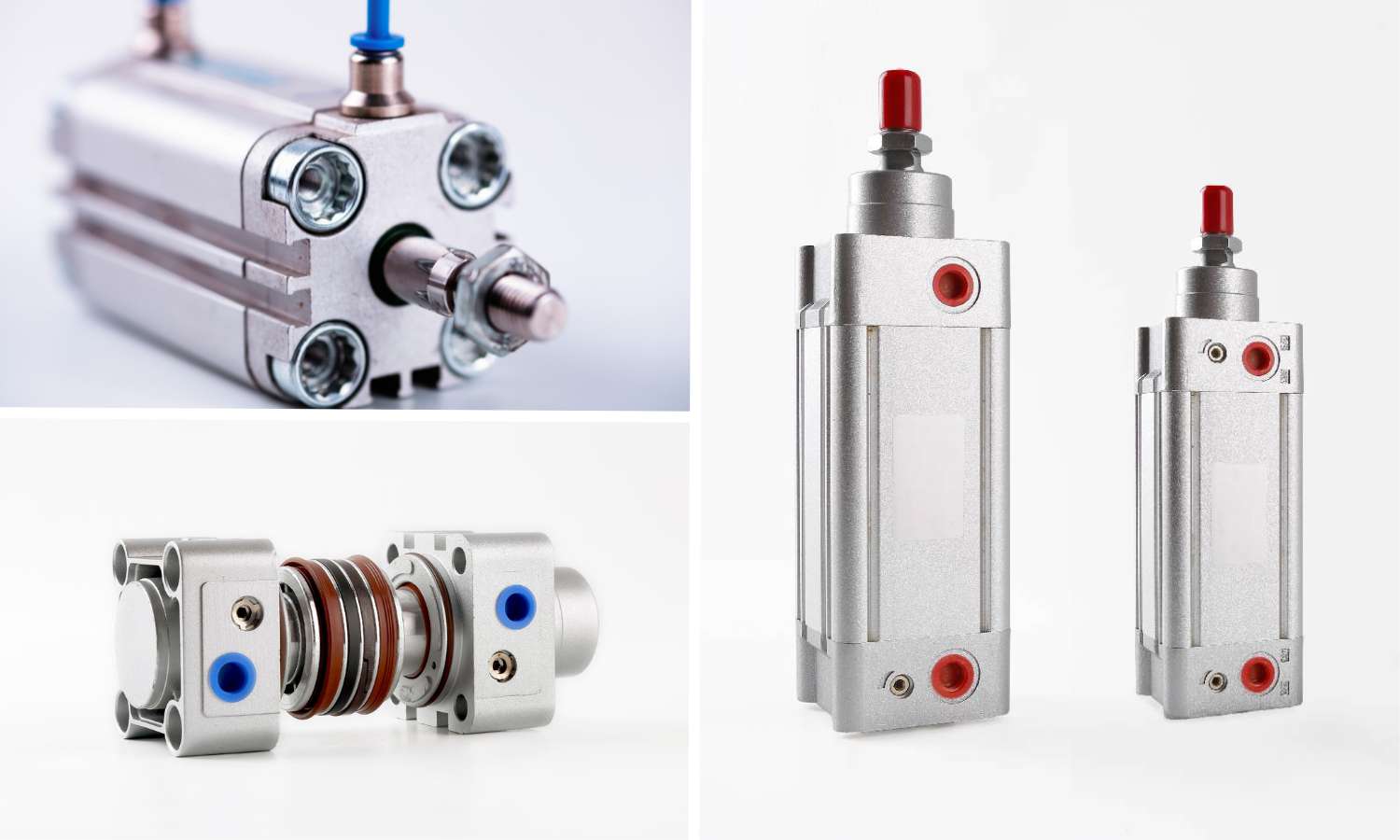
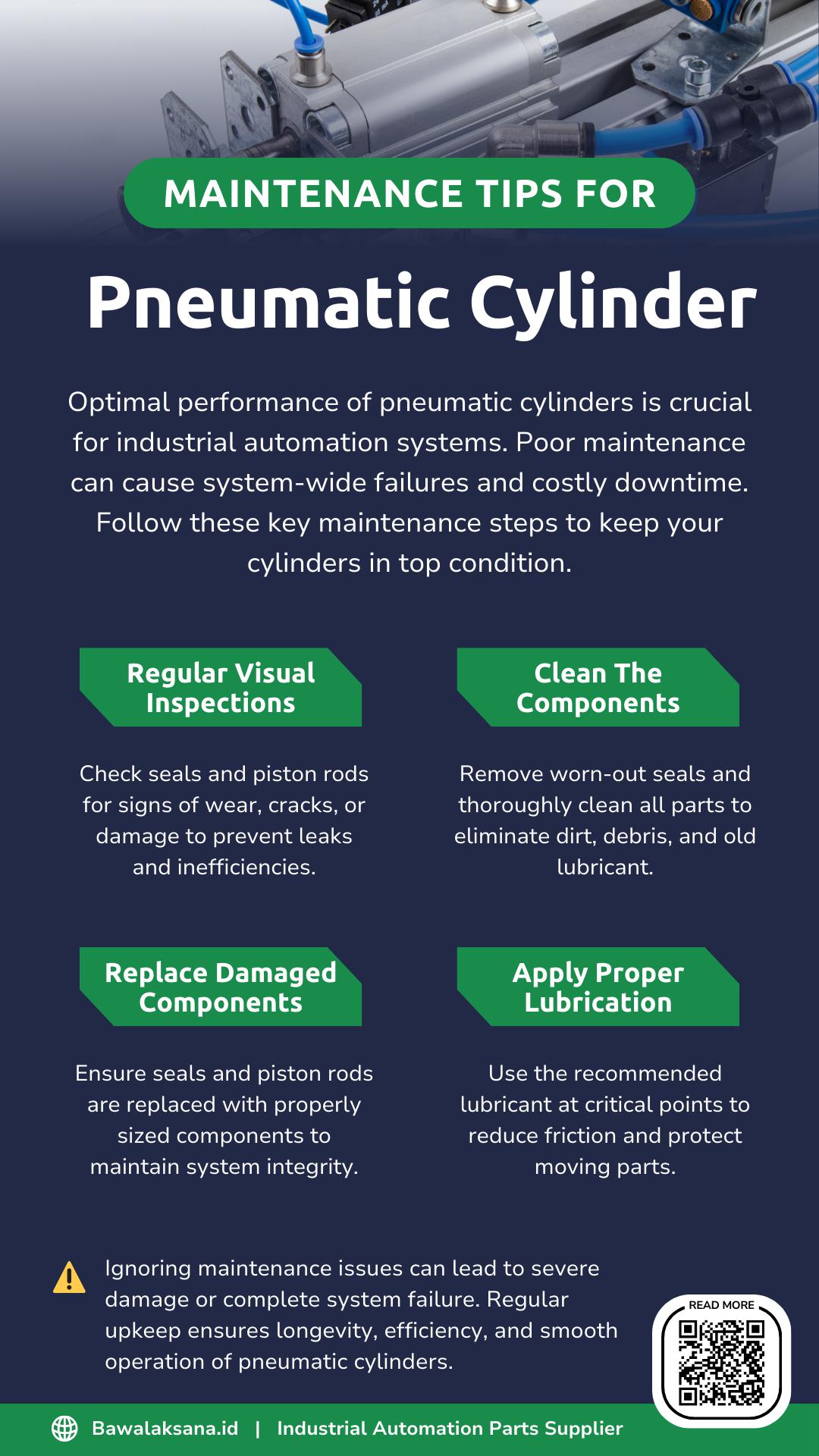
Pneumatic cylinders function as the principal actuators within pneumatic systems. Although engineered for high durability, specific internal components may encounter operational issues. Seals, gaskets, and piston rods are among the components most frequently susceptible to damage.
Moreover, the frequency of usage cycles can exacerbate wear and tear, ultimately leading to component failure, particularly in the absence of regular maintenance.
The potential for failure in pneumatic actuators is a constant concern. Instead of replacing the entire unit each time a problem arises, it is empowering to implement routine maintenance and replace individual cylinder components as required.
The central premise is that proactive and preventive measures are preferable to merely addressing issues post-incident. For instance, a small air leak in a seal, if left unattended, can lead to a complete seal failure, causing a system shutdown and costly downtime. By addressing such issues proactively, you can reduce the risk of such disruptive downtime and the associated increased expenditures.
This article aims to provide insights into the maintenance of pneumatic cylinders, emphasizing the essential components that warrant attention to ensure durability and optimal performance. The Bawalaksana Central Industrial team, a group of experienced professionals in the field of pneumatic systems, will share valuable recommendations regarding best practices in pneumatic cylinder maintenance.
The Importance of Regular Maintenance for Pneumatic Cylinders
Even though pneumatic components, including air cylinders, are engineered for exceptional durability, this resilience does not imply that regular monitoring and maintenance should be neglected. On the contrary, it is crucial to ensure their continued optimal performance.
We can summarize the advantages of consistently maintaining pneumatic cylinders in four critical points below:
- Enhancing performance and prolonging the lifespan of pneumatic cylinders.
- Reducing operational costs by circumventing the need for new pneumatic cylinder units, which can be financially burdensome.
- Facilitating early detection of issues to avert more significant damage.
- Preventing unplanned downtimes, which may result in substantially increased expenditures.
It is essential to recognize that each pneumatic component, including the air service unit, water separator, pneumatic tubing, valves, and pneumatic cylinders situated at the terminus of the pneumatic system, requires specific care and attention.
When maintaining pneumatic equipment, it is imperative to consult the manufacturer’s documentation to guarantee adequate upkeep and mitigate the risk of further damage.
Furthermore, one must remain vigilant regarding common pitfalls in pneumatic system maintenance, such as improper procedures, neglect of safety measures, and the omission of routine inspections.
External Factors Impacting Cylinder Performance
Before discussing the measures needed to maintain pneumatic cylinders, it is crucial to understand the external factors that hinder their performance. Two primary external factors are:
- Extreme Temperatures (both high and low)
- Humidity
Both factors can accelerate the wear of cylinder components or result in substantial damage. The table below summarizes potential issues arising from these factors, along with recommended solutions:
| External Factor | Potential Damage | Recommendations |
| Extreme Temperatures | • Elevated temperatures can expedite the deterioration of cylinder components, such as pistons, seals, and gaskets. • Variations in lubricant viscosity may occur, with thinning at high temperatures or thickening at low temperatures. • The occurrence of water vapor freezing in cold conditions can obstruct airflow. | • Select pneumatic cylinders constructed from materials and seals appropriate for the intended temperature range. • Utilize specialized lubricants. • Consider installing heating or cooling systems when operational requirements require them. |
| Humidity | • The water accumulation inside the cylinder may lead to a hydro lock, damaging the piston and cylinder tube. • Moisture may erode lubricants or grease, accelerating wear and corrosion. • Humidity creates a favorable environment for mold, bacteria, and contaminants, potentially compromising production quality. • In low-temperature scenarios, moisture may freeze, restricting the cylinder’s air supply. | • Implement an efficient air drying system. • Install high-quality filtration, regulation, and lubrication (FRL) units and conduct routine maintenance. • Incorporate drain valves and water separators, regularly removing accumulated moisture at critical junctures. |
When the pneumatic system faces these external factors, it is advisable to increase the frequency of maintenance to mitigate the risk of potential failures.
Furthermore, to tackle the challenges posed by humidity, we have created a comprehensive guide titled “How to Remove Water from a Pneumatic System.” This guide aims to address the ongoing issues related to moisture buildup effectively.
Indicators of Necessary Maintenance for Pneumatic Cylinders
The preceding sections addressed the significance of maintaining air cylinders and the external factors influencing their efficacy.
This section aims to delineate the primary warning signs that suggest a pneumatic cylinder requires immediate maintenance and identify the components that may need to be replaced.
Notably, the frequency of maintenance is contingent upon operating conditions and usage cycles. Nonetheless, there are instances in which a cylinder may necessitate maintenance earlier than anticipated should the following indicators present themselves:
Hissing Sound Due to Air Leakage
A hissing noise during cylinder operation often indicates an air leak in the rod seal at the cylinder head (front cap). This can be caused by:
- High temperatures and frequent usage cycles
- Lack of lubrication
A leaking rod seal leads to energy wastage, as the cylinder requires more compressed air to complete its stroke—particularly during the retraction movement.
Slow or Weak Motion
Several factors may contribute to a pneumatic cylinder’s slow or weak
operation and an eventual cessation of movement. These factors include:
- Damaged piston seals
- Insufficient lubrication
- Blockages in the air supply ports
Should the airports be unobstructed, the underlying issue will likely be associated with either the piston seals or inadequate lubrication. A compromised piston seal permits air from the intake chamber (plus chamber) to leak into the output chamber (minus chamber), diminishing the cylinder’s efficiency during the extension and retraction phases.
Additionally, damage to the piston seal may result in erratic motion, excessive resistance, or the piston making direct contact with the cylinder barrel.
Excessive Noise
Loud noises can occur when lubrication within the pneumatic actuator is insufficient. This typically happens when the grease has dried out, increasing friction between metal components and seals.
If left unaddressed, the friction will worsen, causing the actuator’s stroke to become jerky or noisy during extension and retraction movements.
This condition also leads to higher energy consumption, as the cylinder requires more compressed air to complete its motion.
Cylinder Movement Fluctuations
Industrial automation systems depend on precise and synchronized pneumatic cylinder movements to maintain operational efficiency and accuracy. When a cylinder experiences fluctuations or pulsations in its stroke, it disrupts the automation process, potentially resulting in production defects or system failures.
Indicators of movement fluctuations include:
- Irregular stroke motion
- Slow or sluggish movement
- Sudden stops
- Unpredictable movement
This phenomenon is called slip-stick and is characterized by the cylinder’s jerky and inconsistent motion, which is often attributed to insufficient lubrication.
Should these issues arise, they indicate that the cylinder necessitates immediate maintenance.
Rusty or Bent Piston Rods in Pneumatic Cylinders
THarsh industrial environments can significantly accelerate the corrosion of pneumatic cylinders. Among the most prevalent contributing factors are:
- High humidity and extreme temperatures
- Exposure to chemicals
- Presence of dust or contaminants
- Proximity to welding sparks or open flames
- Implementation of side-loading
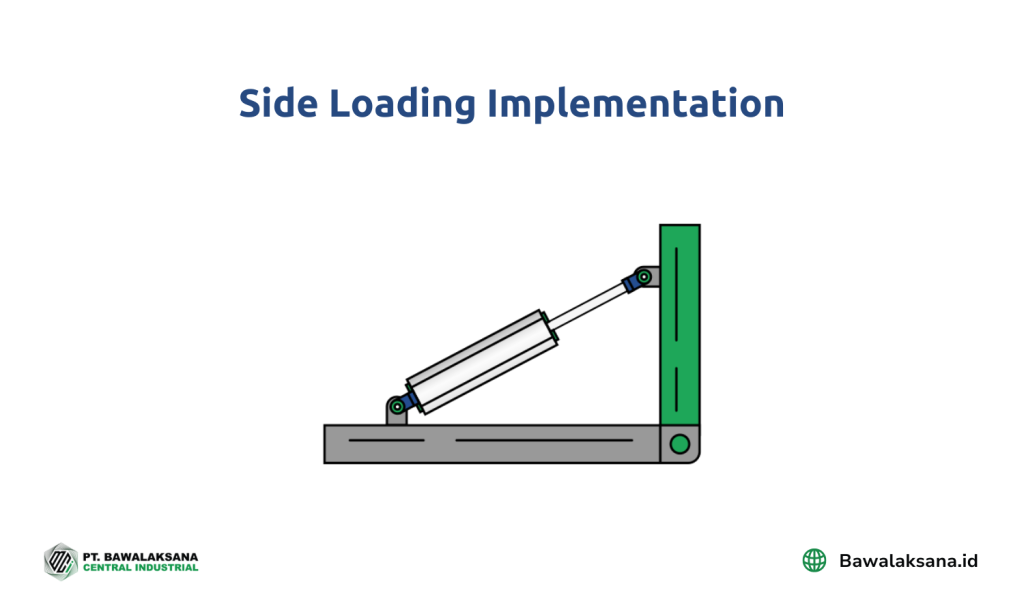
Various industrial challenges lead to the corrosion and deterioration of piston rods, with side loading being a particularly crucial aspect to monitor.
Side loading occurs when an external force is applied to the cylinder rod at an angle. This can bend the piston rod and cause uneven wear on the seals.
No matter how a pneumatic actuator is used, it’s vital to adjust the frequency of maintenance based on operational needs. The following section will delve deeper into this critical topic.
Pneumatic Cylinder Maintenance Procedures
It’s important to understand that each manufacturer may have specific guidelines regarding maintenance procedures, disassembly, lubrication types, and spare part specifications for pneumatic cylinders.
The advice provided here is a general guideline for effectively maintaining pneumatic cylinders. Follow the maintenance instructions from your pneumatic cylinder vendor or manufacturer to ensure proper care and achieve optimal performance.
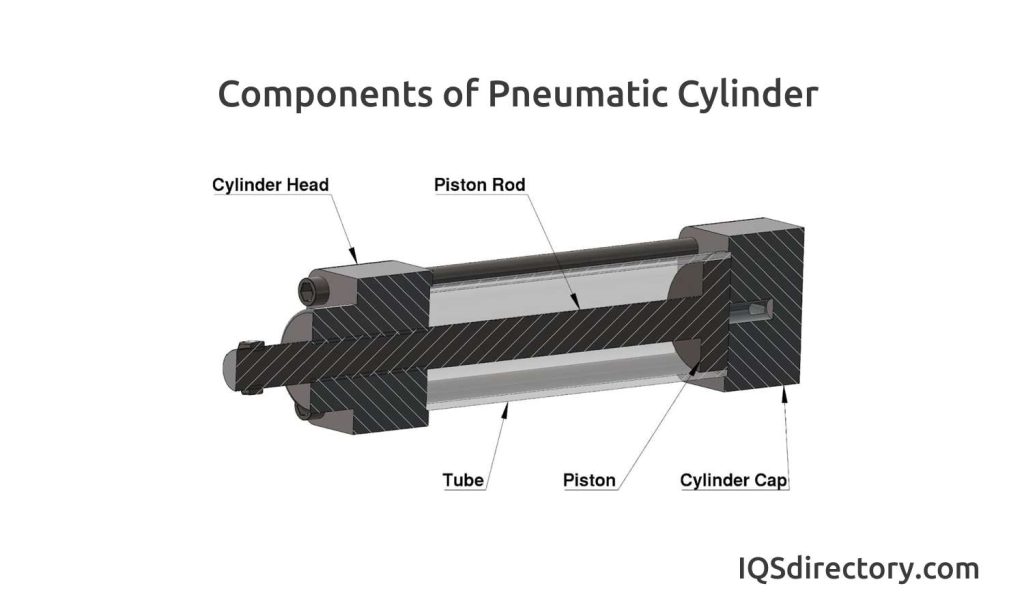
Inspection of Seals and Piston Rods in Pneumatic Cylinders
The initial step in maintaining pneumatic cylinders involves visually inspecting the seals and piston rods, as these components are particularly vulnerable to wear and damage.
A thorough examination of their condition is essential to assess whether they are worn, scratched, contaminated, or need replacement.
Seals in pneumatic cylinders serve as a barrier that prevents the escape of pressurized air from the cylinder while simultaneously blocking external contaminants from entering the cylinder chamber.
Should a seal become compromised, air leakage may occur, accumulating dirt inside the cylinder, which can adversely affect the movement of components.
During the inspection, you must examine the seal on the front cap and assess the piston rod for dirt, scratches, rust, or bending.
Seal damage may manifest as cracks, tears, or breakage, while the piston rod may exhibit signs of rust, scratches, or deformation. Seals are also found in other components of the pneumatic cylinder, such as the piston head.
Suppose the seal on the front cap is damaged. This can negatively impact the performance of other seals within the cylinder, as its function is critical in preventing dust and debris from entering the cylinder chamber.
Consequently, upon detecting any indicators of seal damage, such as tears or leaks, you must disassemble the cylinder and thoroughly clean it to restore functionality and prevent further issues.
The formation of rust on the piston rod can be attributed to several key factors, each contributing to the corrosion process:
- The presence of moist and unfiltered air within the pneumatic system can compromise the protective lubrication on the piston rod, thereby enhancing the risk of rust development.
- Extreme environmental conditions, including elevated temperatures, dust exposure, water splashes, interaction with aggressive chemicals, or exposure to sparks, can adversely affect the integrity of the piston rod.
- Frequent usage cycles may lead to the rapid depletion of lubrication on seals and piston rods. This deficiency can result in metal-to-metal contact, causing scratches and abrasions on the piston rod’s surface.
- Using incompatible pneumatic oils or greases can damage seals and gaskets, rendering them soft and fragile. Such deterioration hampers their ability to effectively reduce friction, further exacerbating the wear on the piston rod.

Disassembling and Cleaning a Pneumatic Cylinder
Adhering to established industrial safety protocols is imperative before disassembling a pneumatic cylinder. Appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, protective clothing, helmets, safety footwear, and safety glasses, is strongly advised.
Furthermore, it is essential to refer to the pneumatic equipment vendor’s maintenance manual and strictly adhere to the specified disassembly and reassembly sequences for all cylinder components.
Key Considerations for Cleaning a Pneumatic Cylinder
Regular cleaning of the pneumatic cylinder is critical, mainly when it operates within environments characterized by dust, dirt, elevated temperatures, or high humidity levels. To facilitate effective maintenance, please consider the following key aspects:
- Establish a clean and organized workspace, arranging all components properly to prevent misplacement, contamination, or assembly errors during reinstallation.
- Utilize the appropriate tools as the vendor recommends during the disassembly and reassembly.
- Wipe the inner and outer surfaces of the cylinder tube with a soft, lint-free cloth, effectively removing dust, oil, grease, and other contaminants.
- Utilize a suitable solvent to eliminate stubborn dirt, ensuring that the chosen solvent is compatible with the cylinder material to avoid potential damage.
- Thoroughly remove any residual lubricant to prevent contamination of new lubricant applications. If moisture or water is present within the cylinder tube, it must be dried entirely.
- Inspect the air passageways (intake and output) for dirt accumulation and ensure you clean them to eliminate residue or blockages.
- Consider installing a protective cover to safeguard cylinders subjected to extreme environmental conditions, such as high temperatures, welding sparks, or chemical exposure.
- Conduct a thorough inspection of the cylinder tube and piston rod for any early signs of wear or damage, including scratches, dents, or deformations.
Adhering to these guidelines effectively prolongs the lifespan of the pneumatic cylinder and maintains its optimal performance in demanding industrial settings.
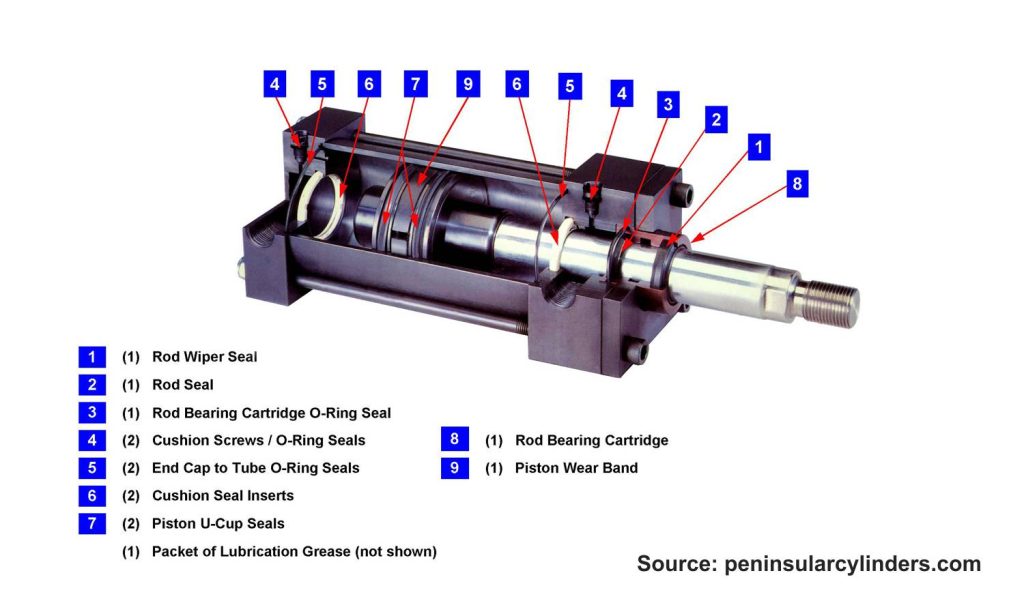
Replacing Damaged Seals
Upon thoroughly cleaning all components within the cylinder, you may replace all seals and gaskets situated at various locations. A pneumatic cylinder may encompass six or more distinct types of seals, contingent upon its design, dimensions, and manufacturer. The most prevalent seals include the following:
- Rod wiper seal (1x)
- Rod seal (1x)
- Rod-bearing cartridge O-ring seal (1x)
- Cap O-ring seals (2x)
- Cushion seals (2x)
- Piston seals (2x)
Cylinder seal lifespan can vary significantly depending on the type of cylinder and the workload applied. Suppose damage to the seals is left unattended for too long. In that case, it can lead to wasted energy and put added strain on the air compressor, which can ultimately drive up operational costs considerably.
We recommend replacing all cylinder seals during scheduled maintenance whenever possible. This strategy promotes a more consistent lifespan across the seals and streamlines the maintenance process, making it more cost-effective and efficient.
Factors That Accelerate Seal Wear
Based on our extensive experience, below are five principal factors that contribute to the accelerated degradation of seals and gaskets in pneumatic cylinders:
- External Factors: Elements beyond control, such as temperature and humidity, can adversely impact cylinder efficiency, culminating in corrosion and irreversible damage.
- Contaminated Operating Environments: Dirt and dust can enhance friction between the seal and piston rod, accelerating component wear.
- Misaligned Piston Rod: Misalignment or side loading can induce uneven wear on one side of the seal, resulting in gaps that permit air leakage and contaminants’ ingress.
- Inadequate Lubrication: Lack of lubrication, especially in high-speed operations, high temperatures, and frequent usage cycles. The damage can worsen if the type of oil or lubricant is incompatible with the seal material.
- Excessive Loading: Continuous loads that exceed the cylinder’s capacity generate heightened friction on seals, pistons, and piston rods.
If any indications of seal damage become apparent, it is crucial to promptly replace the affected seals according to the specifications outlined by the manufacturer. This ensures optimal performance and safety of the equipment.
We also recommend that you conduct a thorough inspection to assess the extent of the damage and follow all relevant guidelines during the replacement process to maintain the integrity of the system and prevent potential failures in the future.
Replacing a Worn, Rusted, or Bent Piston Rod
In addition to keeping the seals in good condition, it’s equally important to monitor the state of the piston rod.
Under conditions of high usage and extreme environments, piston rods can suffer from bending, wear, and rust due to several factors:
- Contaminated or Humid Air: Dirty and moist air can speed up corrosion.
- Harsh Conditions: Elevated temperatures and dusty environments can compromise the piston rod’s integrity.
- Frequent Usage: Operating the machinery frequently can cause seals and piston rods to dry out more quickly.
- Incompatible Pneumatic Oil: Using lubricants that don’t match the cylinder seal materials can lead to premature wear.
- Side Loading with Heavy Loads: Off-center loading can apply excessive force on the piston rod, resulting in bending or uneven wear.
Replacing the piston rod can be a more economical option than buying a brand-new cylinder unit. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the new piston rod aligns with the specifications of your existing cylinder.
Lubricating Cylinder Components
Proper lubrication of the internal parts of a pneumatic cylinder is crucial for ensuring smooth operation, enhancing efficiency, and protecting against corrosion. By applying lubrication in the right places, you help maintain the stability of seals, making them more durable and long-lasting.
Conversely, incorrect lubrication can result in slip-stick motion—jerky movements that can disrupt performance—damage to the seals and scratches on the cylinder rod.
Please remember that careful lubrication is essential for automation systems that depend on precise movements from pneumatic cylinders and should never be taken lightly.
The aim is straightforward: to boost production efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and optimize overall operation.
Here are some key points to consider regarding lubrication in pneumatic cylinder components:
- Lubrication reduces friction between moving parts, preventing slip-stick motion.
- It guards against corrosion and extends the lifespan of the cylinder.
- Proper lubrication enhances device performance and helps avoid premature seal damage that can lead to air leaks.
- Using a lubricant that isn’t compatible with seal materials can increase wear and result in air leaks.
- Insufficient lubrication can compromise the accuracy of cylinder movements.
- It’s worth noting that not all cylinder types require heavy lubrication except in high-cycle applications or extreme environments.
For a more detailed explanation of this topic, check out our comprehensive guide, “Improper Lubrication Can Damage Pneumatic Cylinders,” available on our page.
Reassembling and Function Testing of the Cylinder
Once you’ve lubricated the pneumatic cylinder, the next step is to reassemble it and test its functionality following maintenance according to the manufacturer’s manual.
Before reinstalling the cylinder into the pneumatic system, make sure to double-check the following aspects:
- Seal Position Check: Confirm that all seals are correctly installed, seated properly, and not misaligned or inverted.
- Seal Compatibility: Ensure that the seals match the specific cylinder type and meet the operational load requirements while verifying that you use high-quality materials.
- Manual Movement Test: Before connecting to the air supply, manually extend and retract the cylinder several times to evenly spread the lubricant.
- Leak Inspection: Attach the pneumatic cylinder to the air compressor and thoroughly check for leaks or unusual metal-to-metal friction sounds.
- Noise & Motion Evaluation: Be attentive for any squeaking, jerky movements, or excessive noise, which could signal insufficient lubrication or improper seal installation.

Monitoring, Maintenance Schedule & Documentation
Consistent monitoring and a well-organized maintenance schedule are crucial for ensuring the durability and longevity of pneumatic cylinders. Routine inspections play a vital role in catching early signs of wear, potential leaks, performance issues, and inadequate lubrication.
Essential components to check regularly include:
- Visible Seals: Look for signs of damage, softening, or hardening.
- Piston Rod: Inspect for rust, scratches, or any bending.
- Cylinder Performance: Watch for slip-stick motion, sluggish movement, or resistance.
- Unusual Noises: Be alert for squeaks, rattles, or other abnormal sounds.
What About the Pneumatic Cylinder Maintenance Schedule?
The frequency of maintenance will depend on your company’s operational conditions, and you can categorize it as daily, weekly, or monthly tasks.
- Light Maintenance: Includes routine cleaning of the cylinder’s exterior and applying oil to the piston rod as needed.
- Heavy Maintenance: Requires disassembling the cylinder for thorough cleaning and replacing worn parts.
The need for maintenance should ramp up if environmental challenges arise, such as:
- High air humidity levels
- Extreme conditions (like high temperatures, dust exposure, water splashes, aggressive chemicals, or vulnerability to sparks)
- High cycle rates
Increasing maintenance intensity is essential to ensure optimal cylinder performance when these factors become common.
Is Maintenance Documentation Necessary?
Proper documentation is a vital part of pneumatic cylinder maintenance. It should encompass:
- Lubrication schedules
- Logs of disassembly, cleaning, and parts replacements
- Records of performed maintenance activities
- Noted issues and suggested actions
Detailed, well-maintained records provide a valuable reference for implementing Predictive Maintenance effectively. It’s important to remember that pneumatic cylinders are the most downstream component of the pneumatic system. Keeping them operating at peak performance directly contributes to energy efficiency and productivity on the factory floor.
Recognizing cylinders’ essential role in enhancing your company’s productivity, Bawalaksana.id has put together a comprehensive guide on Boosting Energy Efficiency in Pneumatic Systems for Sustainable Manufacturing.
This guide explores the key factors affecting pneumatic system efficiency and presents strategic measures to optimize performance. For a detailed explanation, click the link above.

Training for the Maintenance Team
Pneumatic actuator technology is one of the fastest-growing elements in industrial automation. These devices provide exceptional flexibility and integrate smoothly with modern technologies and real-world applications.
For this reason, such technology should be maintained by trained professionals who have obtained the necessary certification or received proper training.
The required training focuses on developing a thorough understanding of the technical aspects of pneumatic systems. By learning from industry experts, your maintenance team can tap into the knowledge shared by specialists with vast experience across various industrial sectors. This includes valuable insights from representatives of the vendors supplying your pneumatic equipment.
Such training offers your team essential knowledge to enhance system performance. Most importantly, it helps reduce negligence, minimize human errors, and prepare for potential challenges that may arise in the field.

Conclusion
In summary, while pneumatic cylinders are built for high durability, they still need regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and sustained productivity on the factory floor. It’s crucial to understand that harsh environmental conditions can significantly accelerate wear and tear on cylinder components. Thus, consistent and routine upkeep is key.
PT. Bawalaksana Central Industrial is a seasoned industrial parts supplier with over seven years of experience. We are an authorized distributor for renowned brands such as Metal Work Pneumatic, Mebra Plastik Italia, and Instruments To Industry (ITI).
We offer comprehensive solutions for advanced pneumatic automation systems and high-quality industrial hoses, tubing, and pressure gauges. With robust partnerships across Asia and Europe, we are well-equipped to help boost productivity and efficiency in your operations.
Over 100 major companies in Indonesia, including Petrokimia Gresik, Petronas, and Tempo Scan, trust us for their needs.
If you need expert support in industrial automation systems driven by pneumatics, our team is ready to help.
Reach out to us for tailored recommendations that suit your requirements.

Romanta Pinrih Linuwih
Pneumatic Automation Systems Expert
This article was written in collaboration with Romanta Pinrih Linuwih, an expert in Pneumatic Automation Systems, to ensure accuracy and high quality insights.






![10+ Examples of Pneumatic Tools in Daily Life and Industry [2025]](https://bawalaksana.co/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Sandblasting-large-diameter-pipes-to-remove-surface-contaminants-1080x675.jpg)