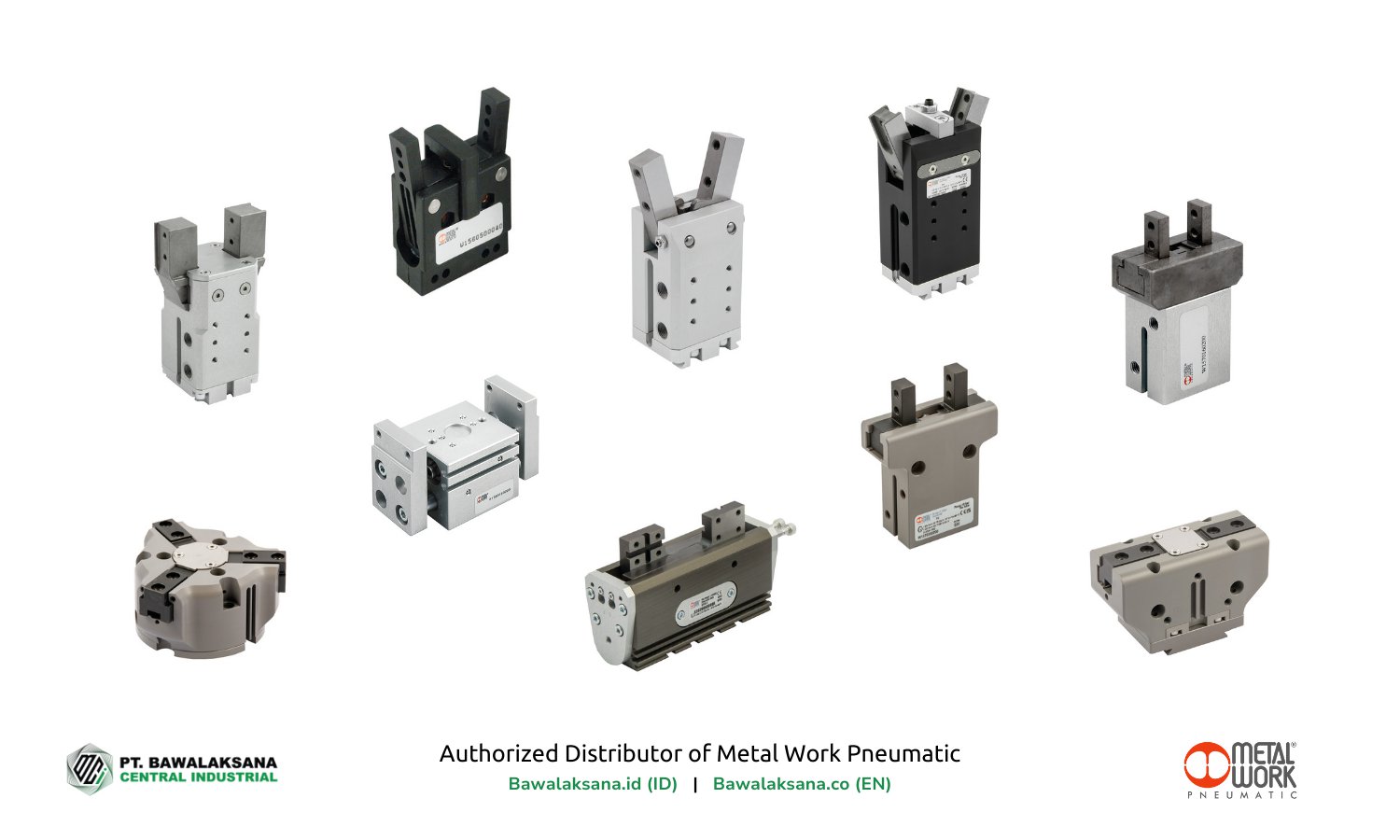
Pneumatic Gripper is a mechanical device powered by compressed air for material handling in industrial applications. Its function is for pick and place, assembly, testing and various other automated jobs on the production line.
These pneumatically powered grippers are often used to improve the interaction of a robot arm with various objects on a production line or to penetrate into areas that are relatively limited to humans.
Pneumatic Gripper is an advanced technology of pneumatic automation system to complete repetitive work quickly, effectively and automatically.
In this article, the Bawalaksana.id team wants to explain what a pneumatic gripper is, its types and functions for industry.
What is a Pneumatic Gripper and Its Function for Industry?
A Pneumatic Gripper is a pneumatically powered mechanical device used on assembly lines in manufacturing to perform various material handling tasks automatically. This technology is usually mounted on the end of a robot arm, such as the Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm or Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm (SCARA).
The functions of the Pneumatic Gripper include gripping, lifting, holding, rotating, assembling, testing and placing objects at specified locations.
Today’s Pneumatic Gripper technology is equipped with controls, sensors and feedback connectivity to ensure precise and accurate movements.

Pneumatic Gripper Anatomy and Basic Formulas to Know
Understanding the nomenclature or anatomy of the Pneumatic Gripper is the most basic thing to be able to apply this device properly on the production line.
We will mention some of the main parts of the Pneumatic Gripper with our main reference being the product catalogs Metal Work Pneumatic.
For your information, Metal Work is one of the pioneers for pneumatic component manufacturing and technology based in Brescia, Italy, with more than 50 years of experience.
The following nomenclature will serve as a reference for you in determining the right type of gripper according to the industrial application and work surface to be handled.
Main Parts of Pneumatic Gripper
The following are the parts of the Pneumatic Gripper with reference to Figure 1.1.
- Pneumatic Gripper: The main part of the gripper that contains a pneumatic cylinder as the core of the jaws drive.
- Jaws: Jaws that move symmetrically to clamp the work object.
- Clamping Finger: Fingers mounted on the jaws that clamp and make contact with the work object.
- Sensor Slot: A place to install a sensor (usually a proximity or reed sensor) to detect the jaw position (open or closed).
- Clamping Force (F): Represents the clamping force for one jaw in units of Newton (N).
- Load: The load or work object clamped by the jaws
- Distance (L): It is the distance between the center point of the object (barycentre) and the reference surface of the gripper. The larger the value of L, the higher the working moment (M).
- Stroke (C): Length of stroke per one jaw when opening and closing.
- Axial Force (Fa): The maximum axial force that the gripper can accept along the vertical axis.
We need to inform you that each type of gripper has a different F or clamping force that is influenced by many factors.
The heavier the jaws, the heavier the load on the gripper so that the F or grip is reduced.
Every Pneumatic Gripper product will definitely provide information on how many F for each jaw, so you can find out how much the Clamping Force of a gripper is.
For example:
If a gripper has 3 jaws and each jaw has F = 25 N, then how much clamping force does the gripper have?
The calculation is as follows:
Clamping Force = 25 × 3 = 75 N.
By knowing the Clamping Force (F), you can estimate how much weight can be lifted according to the number of jaws the gripper has.
To get a more accurate calculation, here we will provide a basic formula in calculating how much F is appropriate to lift an object with a specific load.

Basic Formula for Calculating Gripping Power (F) According to Object Weight
In industrial applications, the Pneumatic Gripper will lift objects with a specific load. For the gripper to operate properly, you need to adjust the clamping force based on the weight of the object being lifted.
As for the accurate Clamping Force calculation, please refer to the Precision Computing Method as shown above.
You can also use a simple formula (Approximation Method) in determining how much Clamping Force (F) to lift an object properly. Clamping Force or F uses Newton (N) units and applies to 1 (one) jaws.
The formula for calculating the Clamping Force (F) based on the mass of the object is as follows:
F ≥ 200 x M/n
M = weight of part (kg)
n = number of jaws
For example:
An assembly line in electronics manufacturing needs to move a component weighing 1.2 Kg using a Pneumatic Gripper that has 3 jaws. What is the Clamping Force (F) for each jaws to be used for the project?
Here are the calculations:
M = 1.2 Kg
n = 3
F ≥ 200 x 1.2 / 3 = 80
Hence, the clamping force for each jaws is 80 N.
You can use the Spread Sheet we have provided to quickly calculate Clamping Force using the Approximation Method. Please access the file Clamping Force Calculation file via Google Spread Sheet.

Types of Pneumatic Gripper for Industry
There are many types of Pneumatic Gripper in terms of shape, function, number of jaws and size.
In general, pneumatically powered grippers have a function to clamp or grip using jaws and clamping fingers.
However, there are also types of grippers with bladder or vacuum suction types that are able to lift an object by utilizing suction power (vacuum).
In the following we will mention several types of jaw-type Pneumatic Gripper that work mechanically thanks to the double/single acting cylinder for gripping and lifting.
Parallel Gripper
The first type is the Parallel Gripper which has two, three or four jaws in parallel. This type of gripper has jaws that move in a straight line and symmetrically and usually uses a double acting cylinder mechanism.
The Parallel Gripper has a strong grip and can lift various shapes of prism or cylindrical objects with a single size.
In certain applications, it is often the case that the objects being lifted have varying diameter sizes. In situations like this, the Parallel Gripper with its three-jaw clamp is the best choice.
Three finger parallel gripper can clamp and lift cylindrical or round objects with different diameters.

Hinged Gripper
Also called an Angular Gripper or a jaw that has a hinge. This type of gripper has a jaw opening that is not very wide, so there are some limitations when interacting with the work surface.
Among its limitations are the following:
- It cannot capture objects that move linearly or from the side except by adjusting the gripper position (see figure 1.5).
- Less effective for capturing objects that have varying dimensions or diameters (see figure 1.6).
- If the component is cylindrical with varying diameters, the position of the clamped component axis will differ according to its size (see Figure 1.7).
Hinged grippers generally move along a circular arc (see figure 1.5) and are relatively cheaper than parallel grippers.
Gripper with Retracting Jaws
Grippers with fully retractable jaws (sideways opening) can provide a wide jaw opening of up to 180°.
With this capability, the Clamping Finger can open fully against the work surface (object), so that it can capture linearly moving objects (see Figure 1.5).
Toggle Gipper
Hinged gripper with toggle action mechanism to achieve high clamping force. The resulting clamping is permanent, even if no air pressure is supplied, so the component cannot be accidentally released.
With an opening angle of up to 180° and a toggle action, this gripper can function as a retraction clamp (internal gripper). However, the high clamping force is only present at a limited angle.
These are the 4 broad categories of jaw-type Pneumatic Grippers most commonly used in industry for material handling or assembly on production lines.
Next, we will mention a few types of grippers based on their working mechanism.

Types of Gripper Based on Mechanism of Action
The jaw-type Pneumatic Gripper has two types of clamping mechanisms and two types of cylinder working mechanisms. By knowing the type of gripper based on its working mechanism, you can make the best choice according to your application needs.
Clamping Mechanism Using Single or Double-acting Cylinder
Pneumatic Gripper uses a pneumatic actuator or cylinder mechanism to perform clamping and retraction operations.
When pressurized air enters the cylinder chamber inside the gripper, the jaws can actively clamp. To return to its original position, there is a spring mechanism that moves the jaw to open again.
For grippers that use a single-acting cylinder, the clamping force occurs in only one direction, clamping or opening.
As for grippers with double-acting cylinders, the clamping force can occur in two directions, when clamping and opening.
In general, grippers with single-acting cylinders consume less energy. This is natural, as air is only used when the cylinder is actively operating to clamp or open.
If you are interested in knowing the difference between a single acting cylinder and a double acting cylinder, please visit our page, Pneumatic Cylinder Types and Components.
Internal or External Clamping Mechanism
The clamping mechanism is how the gripper device grips an object. An external clamping mechanism uses a force to clamp or grip an object through the outer side of the object.
The analogy is like you grasping a ball or picking up a small object with your fingers. This is what is meant by the external clamping mechanism.
The internal clamping mechanism is used to lift hollow objects from their internal sides. For example, lifting a small class by extending two fingers through the internal side of the glass.
In general, external clamping mechanisms are the most popularly used. However, in complex industrial applications, internal clamping mechanisms are also often used.
Some modern Pneumatic Gripper designs can perform both internal and external clamping mechanisms, making them more flexible for complex manufacturing operations.
In such cases, a gripper with a double-acting cylinder mechanism may be the best choice.

Example of Pneumatic Gripper Application in Industry
In the modern industrial era, Pneumatic Gripper is widely used as a vital automation tool for pick and place, material handling to assembly for various manufacturing processes.
Among the most striking advantages of this technology is that it is lightweight, cost-effective compared to other gripper systems and has great flexibility for jaw design and gripping mode.
Pneumatic-powered grippers are reliable in terms of speed and accuracy. And can complete various kinds of work that are difficult for humans to reach automatically and continuously.
Broadly speaking, Pneumatic Gripper can be applied to various types of work such as:
- Automatic Assembly Machines
- Automatic Testing Machines
- Robotic System for Machine Tool
The reel below is one example of applying a complex gripper and pneumatic system to a Lego toy production line.
With good planning, the functions of the Pneumatic Gripper can be enhanced to handle a variety of complex jobs.
The following are some examples of Pneumatic Gripper applications in various industrial sectors:
- Automotive Industry: Used in conjunction with robotic arms to handle various vehicle parts on assembly lines.
- Toy Manufacturing: Used with complex pneumatic systems to quickly and accurately assemble lego toys.
- F&B industry: Used with robotic arms or complex pneumatic systems to handle hygienic materials from filling, pick and place, to packaging.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Used with robotic arms for fine material handling, automated pick-and-place and assembly.
Pneumatic Gripper technology can be further explored for use in various applications in industry. Especially for handling repetitive tasks quickly and accurately.
With proper planning and implementation, Pneumatic Gripper can help your company to achieve significant economies of scale and sustainable production cycles.

Increase Economies of Scale by Implementing V-Lock System and Pneumatic Gripper
Production scale can be significantly increased effectively and quickly by combining the Pneumatic Gripper and V-Lock System. Using Metal Work’s Pneumatic System Automation technology, the production line can run automatically and seamlessly.
PT. Bawalaksana Central Industrial as Authorized Distributor Metal Work Pneumatic can provide comprehensive and professional support. With an experienced Application Engineer team, we can provide support from planning, implementation to maintenance.
If you have plans to improve economies of scale on the manufacturing floor using pneumatic technology please talk to your Application Engineer team to get the right solution.
Click the consultation button below to start connecting with our professional team now.

Piko Prasetyo
Application Engineer
This article was written in collaboration with Piko Prasetyo, an expert in Automation, Embedded Systems and Artificial Intelligence, to ensure accuracy and high quality insights.




![10+ Examples of Pneumatic Tools in Daily Life and Industry [2025]](https://bawalaksana.co/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Sandblasting-large-diameter-pipes-to-remove-surface-contaminants-1080x675.jpg)


![Problems with 3 Phase Contactors and How to Solve Them [Practical & Effective]](https://bawalaksana.co/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Masalah-Pada-Kontaktor-Motor-3-Phase-dan-Cara-Mengatasinya-Bawalaksana-ID-1080x675.jpg)